Written By Rohit Sati M.Sc., and Deep Gulati P. Eng
Layfield Geosynthetics | May 2024
The term HPOIT was first introduced in 1990 when a new type of stabilizer was introduced to enhance the ultraviolet performance of thin film polymeric products. Hindered Amine Light Stabilizers (HALS) were used to stabilize and protect clear or transparent polyethylene films from degradation due to ultraviolet (UV) light. Later, it’s use was extended into geomembranes to improve UV and oxidative performance. With the new stabilizer came the new ASTM D5885, during ageing the additives are consumed by UV, oxygen or chemical attack, or lost physically due to evaporation, leaching, or migration at the surface. The change in the antioxidant content of the material is measured by ASTM D3895 (for OIT) and/or ASTM D5885 (for HPOIT). These tests are performed on small samples (about 5 mg) at higher temperatures. The HPOIT test runs longer compared to standard OIT test (ASTM D3895). Based on the formulation of the geomembrane sheet, a typical test duration can range anywhere between 100-200 minutes for standard OIT test and between 400-2500 minutes for HPOIT. The primary difference between OIT and HPOIT tests is that the HPOIT testing is conducted at a lower temperature and higher pressure in the test container compared to the standard OIT test.
The precision and bias, also known as uncertainly, is not well established for both standard and high pressure OIT testing. While the standard OIT has been known to consistently produce good reproducible test results, the HPOIT has shown large variation in reproducibility between laboratories. To understand the uncertainty and the variation amongst different laboratories Layfield reviewed both ASTM and GAI-LAP round-robin test data from different geosynthetics laboratories and then used statistical analysis to observe repeatability(r) within the laboratory and reproducibility(R) between labs. As per section 12 of the ASTM D3895-19, round-robin tests were first performed in 1991, when the test was introduced. The data on precision and repeatability is presented in Table 1 of ASTM 3895 which shows results for repeatability and reproducibility performed on HDPE and LLDPE. As per Table 1, the variation between laboratories should not exceed more than 60 mins and 40 mins for HDPE and LLDPE respectively. However, it comes with a word of caution, it states in section 12.2 that “do not apply the data in Table 1 rigorously to acceptance or rejection of material, as those data are specific to the round-robin, and not representative of other lots, condition, materials, or laboratories”. Section 14, precision and bias of ASTM D5885 states that “the two values, each the mean of duplicate determinations, should be considered suspect if they differ by more than 25% between laboratories and 6.5% within laboratories”.
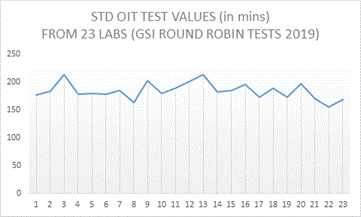
The GAI-LAP program which is managed by the Geosynthetics Institute performs round-robin tests each year. From the results of testing from the 2019 round robin results, it shows good reproducibility in the standard OIT testing to ASTM D3895 however the HPOIT testing shows significant variation. Twenty-three labs participated in round-robin tests for ASTM D3895 and ASTM D5885 respectively. A summary of results for HDPE geomembrane (identified as GM-53) is as follows;
ASTM D 3895, Standard OIT:
Average value = 184 minutes; Standard Deviation = 15
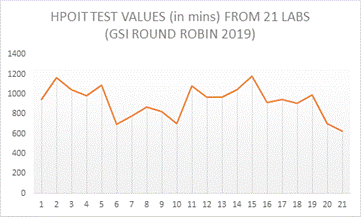
ASTM D 5885 HP OIT:
Average value = 926 minutes. Standard Deviation = 163
In summary, both repeatability (within lab) and reproducibility (between labs) of test methods should be considered when comparing conformance test results to specification. Many projects require third party testing for meeting compliance therefore reproducibility is an important consideration, because it demonstrates that different laboratories can produce varying results under varying conditions. Results from the latest round of testing from GSI show a standard deviation(S.D) of 15 for standard OIT tests and a S.D of 163 for HPOIT test. It can therefore be anticipated that larger variation will exists when calculating HPOIT percentage retention after UV and Oven Ageing exposures. This is because percentage retention standard OIT or HPOIT will include variation from both baseline and exposed test results. To minimize the uncertainly, Layfield recommendsthat testing of the samples, both before and after exposure, be performed by the same lab and preferably on the same equipment that was used for initial OIT and HPOIT testing.
Related Articles
View All News